Control System Design of Ball and Plate
MECA482 - Control System Design
Angel Mendoza, Chen Hung Yang, Jonathan Gomez, Marco Machuca, John Danley
1. Introduction
Description of the project:
The ball and plate system consists of a tiltable plate controlled by two motors at perpendicular orientations with a ball positioned on the plate. The goal is to develop the Simulink model that controls the X and Y axis of the plate system in Coppelia Sim Edu.
Table of Contents
2. Modeling
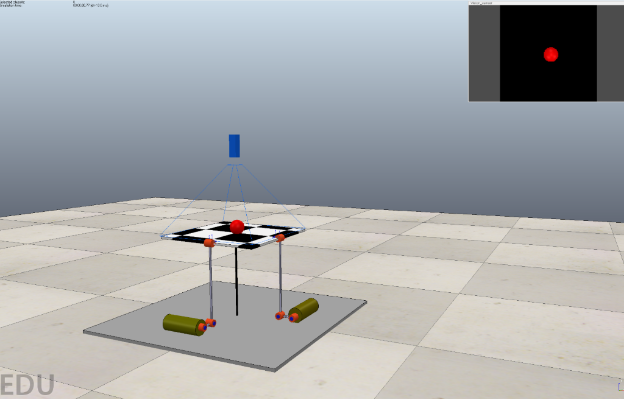
The system is simulated in Coppelia Sim Edu utilizing a plate that is supported by two revolute joints on the individual sides that control the tilting mechanism for the balance of the ball. The control system described is to hold a freely rolling ball in a specific position on the plate using a sensor for a feedback loop to maintain the position of the ball. For measuring the ball position, a camera sensor was used to provide feedback information. To simplify this system, it is modeled as two independent ball and beam systems. This is possible because the x and y positions are only going to be affected by their respective beam angles.
The data is processed in the following way:
- The camera observes the position of the ball in CoppeliaSim and sends the data to Matlab
- Matlab recieves data from Coppelia
- Simulink retrieves the data from the Matlab workspace and calculates the rotation of the motors,
An image of the virtual model produced in CoppeliaSim is shown below:
3. Controller Design and Simulations
A controller was developed to balance the ball on the plate with the following specifications:
- Settling time: Ts ≤ 3.0 (s)
- Percent Overshoot: %OS ≤ 10
The above specifications are used to determine the natural frequency value (ωn) whose equations ar shown below:
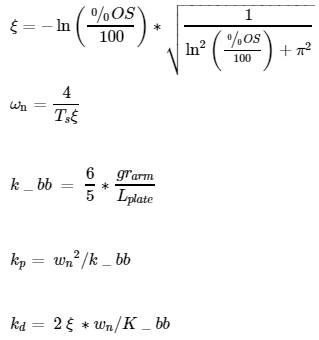
3.1. Force Calculations
To mathematically develop the proper equations to relate the necessary angle of lift on the balance plate (α) to the distance the ball has strayed away from the balance plate’s target location (x). Using the free body diagram below (Figure 1), forces from the ball’s inertia (Fr) and due to gravity on the ball (Fg) can be mapped out to determine the proper functions.
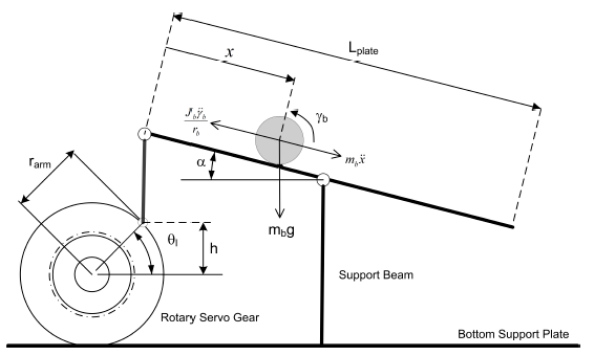
The sum of forces can be written:
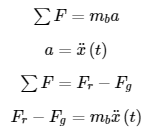
Relating the angle of tilt of the plate (α) to the force on the ball by gravity (Fg) gives the following equation:
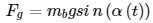
Using torque, an equation can be formed relating force of intertia to ball radius (rb) with the proper torque equaton of the rolling ball:
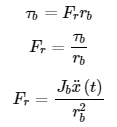
The equation for the hollow ball inertia is given below:
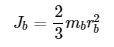
By plugging the ball’s inertia into inertial force (Fr) equation, the new equation is shown below:
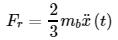
Fr and Fg can be used to construct the new force equation for ball displacement vs lift angle of plate.
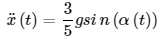
The angle displacements of the plate and motor can be written through trigonometric relationships:
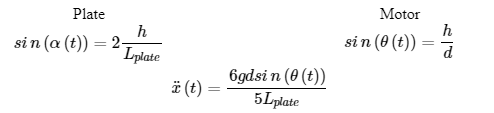
With small angle approximation and laplace transform, the transfer function is given below:
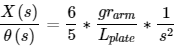
3.2 Input Voltage to Position Change Transfer Function
The block diagram below illustrates the in put of Vm(s) through the servo plant (SRVO2), outputting the servo angle (θ(s)), which in response, adjusts the position of the ball (X(S)) after going through the plant of the balance plate (Pbb(S)):
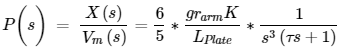
3.3 Motor Parameters to Refine Transfer Function
Using a SRV02, after motor analysis accounting for the motor specifications, the motor’s transfer function is given below:

Where:
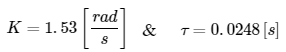
Using the above parameters, the simplified transfer function relating input motor voltage to position change of the ball is given below:
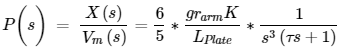
3.4 Coded Simulation
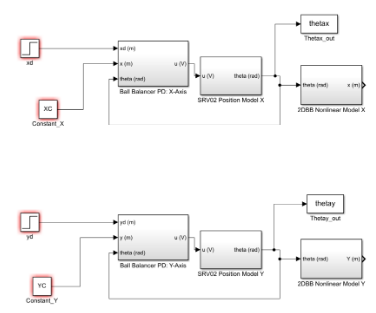
4. Checklist
Deliverables:
- Project Presentation
- Webpage
- Github
- Mathematical model of the system using MATLAB/Simulink
- Show that the algorithm facilitates the design requirements
- Test algorithms on the physical system
5. References
[1] Quanser Inc., 2 DOF Ball Balancer, https://www.quanser.com/products/2-dof-ball-balancer/
[2] Messner, B., Tilbury, D., et al., Control Tutorials for MATLAB & Simulink, http://ctms.engin.umich.edu/CTMS/index.php?aux=Home
[3] Remote API Matlab functions, coppeliarobotics.com/helpFiles/en/remoteApiFunctionsMatlab.htm#simxAddStatusbarMessage
[4] B0-based remote API, Matlab, https://www.coppeliarobotics.com/helpFiles/en/b0RemoteApi-matlab.htm